We have developed biologically informed mathematical models for studying antimalarial drug action and cost-effectiveness models for evaluating screening tests used to determine the safety of the antimalarial treatment, primaquine. Check out our online model simulation software tools to aid decision making regarding treatment regimens and screening tests. Our models are validated on clinical and experimental data (see ACREME website for our extensive network of collaborators) within a Bayesian framework using advanced MCMC algorithms. To improve the design of future studies we have developed a software package that implements a Bayesian Optimal Design method.

Within-host malaria modelling to improve the treatment of malaria
Artemisinin derivatives are the first line treatment for falciparum malaria. Alarmingly, resistance to these drugs has emerged in Southeast Asia, jeopardizing malaria control. … More » about Within-host malaria modelling to improve the treatment of malaria
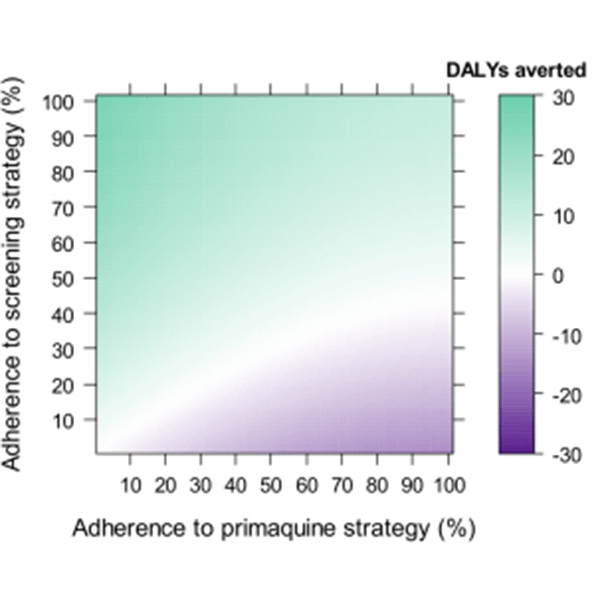
Economic modelling to improve the management of malaria
A single infectious bite with vivax malaria can cause multiple malaria episodes through dormant liver parasites. Radical cure is needed to clear these liver parasites, but the … More » about Economic modelling to improve the management of malaria
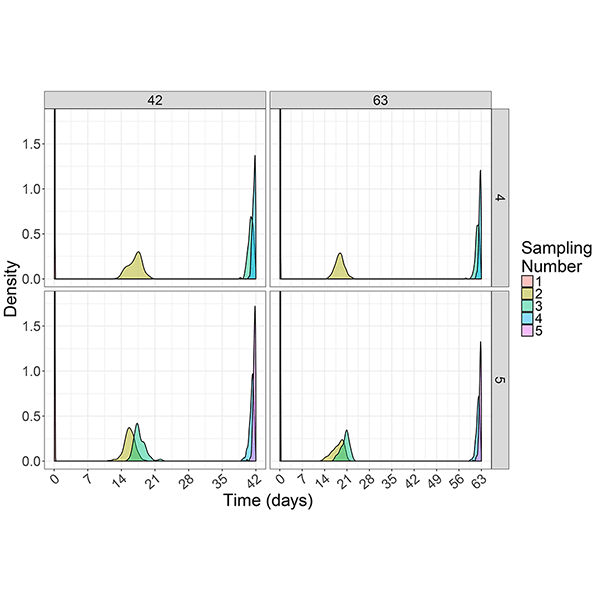
Optimal Sampling Schedules
Pharmacokinetic (PK) studies are routinely used in the study of malaria to understand, for example, how (and for how long) different drugs act on the malaria parasite, so that … More » about Optimal Sampling Schedules
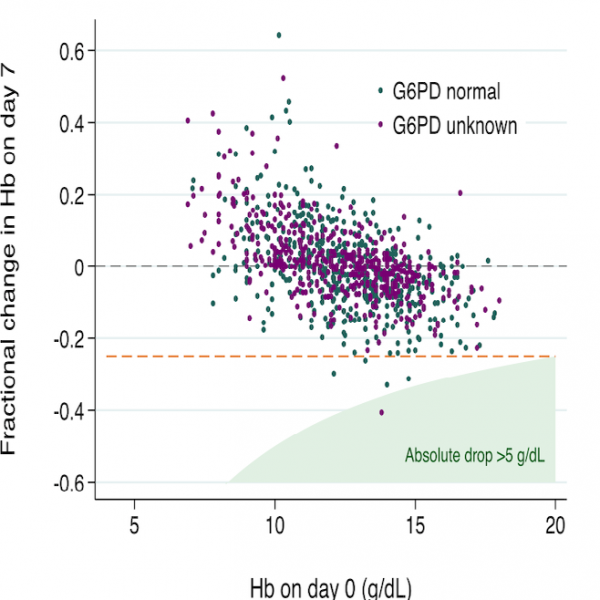
Meta-analyses to inform optimal primaquine radical cure
P. vivax requires radical cure for control of blood and liver stages. Primaquine is the only widely available drug to kill liver stage vivax malaria, however, it can cause … More » about Meta-analyses to inform optimal primaquine radical cure